【深度好文】生產設備PLC/HMI/SCADA的數據完整性風險!
生產設備PLC/HMI/SCADA的數據完整性風險!
GMP范圍內常見的生產與工程的設備的計算機化系統大多以PLC(Program Logic Controller 可編程邏輯控制器),HMI (Human Machine Interface 人機交互界面-觸摸屏),SCADA( Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition即數據采集與監視控制系統)三類形式存在;例如自動壓片機,凍干機,包衣機,純水制備分配及監控系統,環境監測系統。
相比于先前“數據完整性風暴中心”的QC實驗室,生產和工程的計算機化系統更普遍存在著:系統老舊(如仍使用Windows XP),單機版系統多,流程中部件單元多,無數據備份和詳細審計追蹤,權限隔離不清,數據配置可被非法修改刪除等問題。
檢查缺陷
2018年5月24日簽發的FDA 483(FEI 編號 3008565058)中就提及了生產設備數據完整性相關的缺陷:

檢查發現,針對數據完整性:
(公司內)計算機化系統缺乏合適的管控手段來確保生產和控制的主數據和記錄(master production and control records)僅僅能夠被授權人士來修改。
特別指出,貴公司的生產設備不符合21 CFR Part 11:
a. 現階段,有XX個單機版生產設備未能配置合適的HMI/PLC/SCADA系統,因此它們缺少帶時間戳的審計追蹤,數據管理,報警管理,記錄歸檔與恢復等功能;
b. 現階段,有XX個單機版設備有內置的HMI,但是這些HMI缺少帶時間戳的審計追蹤,數據管理,報警管理,記錄歸檔與恢復等功能;
c. 現階段,有XX個單機版設備有內置的SCADA,但是這些SCADA缺少帶時間戳的審計追蹤,數據管理,報警管理,記錄歸檔與恢復等功能;這些設備僅僅可以打印針對CPP(關鍵過程參數)的實時審計追蹤報告用以核對填寫BMR(批次生產記錄)。
PDA期刊:SCADA系統的數據完整性風險
在PDA期刊中刊登了關于SCADA系統的數據完整性風險:
Data Integrity Risks on SCADA Systems
SCADA系統數據完整性性風險
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) software vendors have historically served industries that require tight controls over system configurations and data records. As a result, modern SCADA software systems have evolved to provide a robust set of tools intrinsically designed to prevent the intentional or unintentional undetectable alteration of system data. Most notably, the integration of electronic record management, electronic signatures, logical security, and audit trail functions are built-in or made available as optional features to provide compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11. However, there are several considerations and controls that are worth looking at regarding data integrity.
SCADA(監測控制和數據采集)軟件供應商歷來服務于各個需要嚴格控制系統配置和數據記錄的行業。因此,現代SCADA軟件系統已經發展到能夠提供一套強大的工具,其內在設計可以防止系統數據有意或無意的不可檢測的更改。最值得注意的是,電子記錄管理、電子簽名、邏輯安全和審計追蹤功能的集成是內置的,或作為可選功能,以提供符合 FDA 21 CFR Part 11 的法規。但是,在數據完整性方面有幾個注意事項和控制措施值得關注。
The front line defense is, of course, the security of the process network. Physical security of all network components should be considered in the design of the system. Production facilities, system servers, network switches, PLCs, IO modules, process instrumentation, and where possible, production workstation terminals should be kept under lock-and-key with access limited to as few individuals as necessary to operate and maintain the network hardware systems. Logical security should be limited to a documented list of authorized individuals, with clearly delineated permissions limiting their access to only those system functions commensurate to their level of responsibility and qualification to access or generate data on the system.
當然,前線防御是流程網絡的安全性。在系統設計中應考慮所有網絡組件的物理安全性。生產設施、系統服務器、網絡交換機、PLC、IO模塊、過程儀表,和生產工作站終端(如有)應妥善保管,并且訪問僅限于需要對網絡硬件系統進行操作和維護的人員。邏輯安全應限于經批準的人員,并有正式清單,明確劃分權限限制其訪問權限僅限于與其訪問或生成的責任級別和資格相稱的系統功能系統上的數據。
Clear guidelines for establishing security for a SCADA system are provided in the National Institute of Standards and Technology, Special Publication 800-82, Guide to Industrial Control Systems (ICS) Security (Rev.2, May 2015,https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-82r2.pdf). The document addresses security risks for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, Distributed Control Systems (DCS), and other control system configurations such as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC).
美國標準與技術研究所為SCADA系統安全性的提供了明確的指南, 特別出版800-82,工業控制系統 (ICS)安全指南(2015年5月第2版,https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/NIST/NIST.SP.800-82r2.pdf)。該指南包括監測控制和數據采集(SCADA)系統、分布式控制系統(DCS)和其他控制系統配置(如可編程邏輯控制器((PLC))的安全風險。
The Executive Summary of the Guide document offers examples of the types of possible incidents that might occur as a result of data security breaches or a lack of adequate data security on an industrial control system:
《指南》文件舉例說明了由于數據安全漏洞或工業控制系統缺乏足夠的數據安全而可能發生的事件類型:
· Blocked or delayed flow of information through ICS networks, which could disrupt ICS operation.
阻止或延遲ICS 網絡上的信息流,可能導致ICS運行中斷。
· Unauthorized changes to instructions, commands, or alarm thresholds, which could damage, disable, or shut down equipment, create environmental impacts, and/or endanger human life.
對指令、命令或報警值的未經授權的更改,可能會損壞、或使設備失效或停止,造成環境影響和/或危及人的生命。
· Inaccurate information sent to system operators, either to disguise unauthorized changes, or to cause the operators to initiate inappropriate actions, which could have various negative effects.
發送給系統操作員的不準確信息,導致未經授權的更改被掩蓋,或導致操作員采取不恰當的行動,這可能會產生各種負面影響。
· ICS software or configuration settings modified, or ICS software infected with malware, which could have various negative effects.
ICS 軟件或配置設置被修改,或 ICS 軟件感染惡意軟件,這可能會產生各種負面影響。
· Interference with the operation of equipment protection systems, which could endanger costly and difficult-to-replace equipment.
設備保護系統運行受到干擾,可能危及昂貴且難以更換的設備。
· Interference with the operation of safety systems, which could endanger human life.
干擾安全系統運行,可能危及人的生命。
Notably, the Executive Summary does not highlight the potential loss, adulteration, or alteration to process data history stored in a SCADA database. This risk is, however, addressed extensively throughout the document.
值得注意的是,指南沒有強調存儲在 SCADA 數據庫中的工藝數據歷史的潛在丟失、摻假或更改。但是,在整個文件中廣泛討論了這一風險。
The Executive Summary of the Guide document highlights the major security objectives for an ICS:
《指南》強調了ICS的主要安全目標:
· Restricting logical access to the ICS network and network activity.
限制對 ICS 網絡和網絡活動的邏輯訪問。
· Restricting physical access to the ICS network and devices.
限制對 ICS 網絡和設備的物理訪問。
· Protecting individual ICS components from exploitation.
保護各ICS 組件免受攻擊。
· Restricting unauthorized modification of data.
限制未經授權的數據修改。
· Detecting security events and incidents.
檢測安全事件和事故。
· Maintaining functionality during adverse conditions.
在惡劣條件下保持功能。
· Restoring the system after an incident.
發生事故后還原系統。
In a typical ICS this means a defense-in-depth strategy that includes:
在典型的 ICS 中,這意味著深度防御戰略,其中包括:
· Developing security policies, procedures, training and educational material that applies specifically to the ICS.
制定適用于 ICS 的安全政策、程序、培訓和教育材料。
· Considering ICS security policies and procedures based on the Homeland Security Advisory System Threat Level, deploying increasingly heightened security postures as the Threat Level increases.
根據國土安全咨詢系統威脅級別,考慮 ICS 的安全政策和程序,威脅級別越高,安全態勢越嚴格。
· Addressing security throughout the lifecycle of the ICS from architecture design to procurement, to installation to maintenance to decommissioning.
解決 ICS 從架構設計到采購、安裝、維護、退役整個生命周期的安全問題。
· Implementing a network topology for the ICS that has multiple layers, with the most critical communications occurring in the most secure and reliable layer.
為具有多個層的 ICS 實現網絡拓撲,最關鍵的通信發生在最安全可靠的層中。
· Providing logical separation between the corporate and ICS networks (e.g., stateful inspection firewall(s) between the networks, unidirectional gateways).
提供公司網絡和 ICS 網絡之間的邏輯分離(例如,網絡、單向網關之間的有狀態檢查防火墻)。
· Employing a DMZ network architecture (i.e., prevent direct traffic between the corporate and ICS networks).
使用 DMZ 網絡體系結構(即防止公司網絡和 ICS 網絡之間的直接交互)。
· Ensuring that critical components are redundant and are on redundant networks.
確保關鍵組件是冗余的,并且位于冗余網絡上。
· Designing critical systems for graceful degradation (fault tolerant) to prevent catastrophic cascading events.
設計用于功能故障(容錯)的關鍵系統,以防止災難性級聯事件。
· Disabling unused ports and services on ICS devices after testing to assure this will not impact ICS operation.
在測試后禁用 ICS 設備上未使用的端口和服務,以確保這不會影響 ICS 操作。
· Restricting physical access to the ICS network and devices.
限制對 ICS 網絡和設備的物理訪問。
· Restricting ICS user privileges to only those that are required to perform each person’s job (i.e., establishing role-based access control and configuring each role based on the principle of least privilege).
將 ICS 用戶權限限制為僅執行個人工作所需的權限(即建立基于角色的訪問控制和基于權限最小化原則配置每個角色)。
· Using separate authentication mechanisms and credentials for users of the ICS network and the corporate network (i.e., ICS network accounts do not use corporate network user accounts).
對 ICS 網絡使用獨立于公司網絡的用戶身份驗證機制和憑據(即 ICS 網絡帳戶不使用公司網絡用戶帳戶)。
· Using modern technology, such as smart cards for Personal Identity Verification (PIV).
使用現代技術,如用于個人身份驗證 (PIV) 的智能卡。
· Implementing security controls such as intrusion detection software, antivirus software and file integrity checking software, where technically feasible, to prevent, deter, detect, and mitigate the introduction, exposure, and propagation of malicious software to, within, and from the ICS.
實施安全控制,如入侵檢測軟件、防病毒軟件和文件完整性檢查軟件(如果技術上可行),以防止、阻止、檢測和減輕惡意軟件的入侵、暴露和傳播。
· Applying security techniques such as encryption and/or cryptographic hashes to ICS data storage and communications where determined appropriate.
將加密和/或加密哈希等安全技術應用于 ICS 數據存儲和通信(如果確定適當)。
· Expeditiously deploying security patches after testing all patches under field conditions on a test system if possible, before installation on the ICS.
如有可能,在測試環境下測試所有補丁后,在 安裝至ICS 之前盡快部署安全補丁。
· Tracking and monitoring audit trails on critical areas of the ICS.
跟蹤和監測 ICS 關鍵區域的審計追蹤。
· Employing reliable and secure network protocols and services where feasible.
在可行的情況下使用可靠和安全的網絡協議和服務。
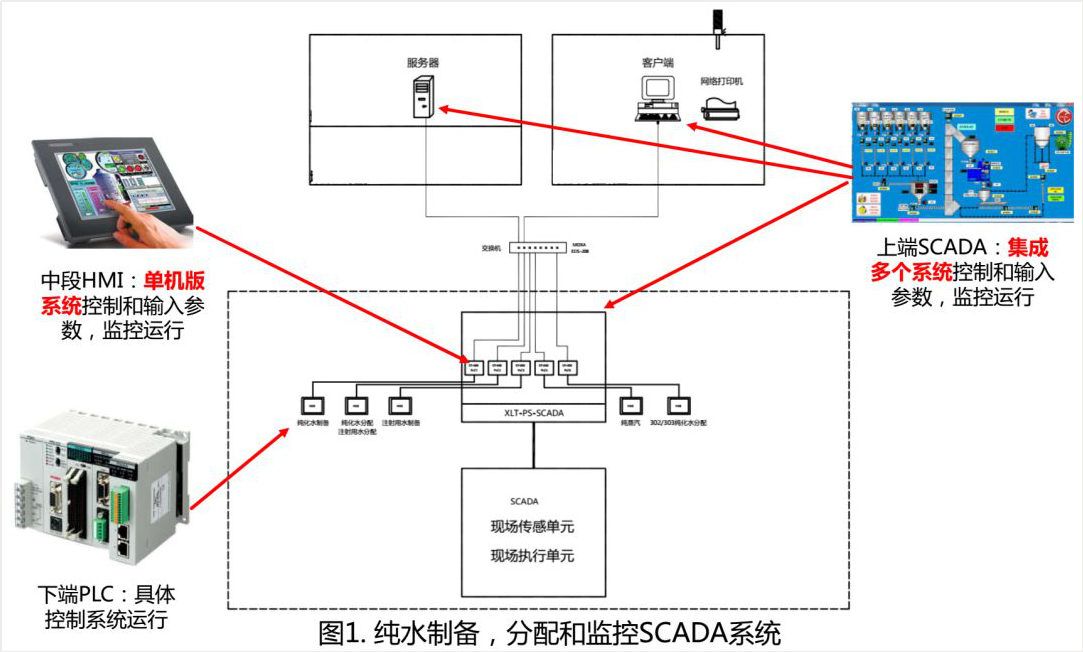
典型的PLC/HMI/SCADA – 系統架構
典型的PLC/HMI/SCADA – 數據流
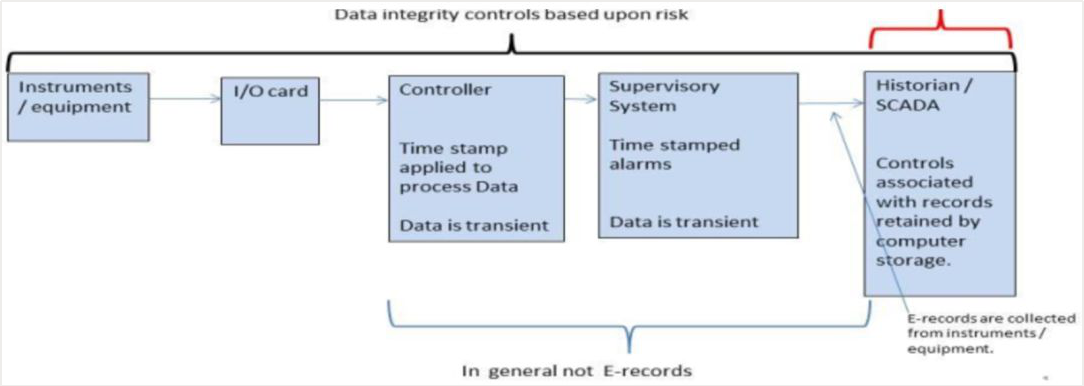
圖2. 典型自動化生產工程系統的數據流示意圖[1]
結合圖1和圖2,在典型的自動化生產和工程系統中:
數據流是:設備持續運行→PLC采集于設備→PLC短暫數據→ HMI(單機版)短暫數據→ SCADA(集成版)存儲數據
21 CFR Part 211.68(b) 與 EU Annex 11 p5 都明確要求:為確保數據完整性,計算機化系統的數據,記錄或者其他信息,其輸入和輸出都必需檢查確認其準確性。 ′為滿足上述期望,(企業)需要定期驗證確認計算機化系統的軟硬件以及接口,來確保直接來源設備的數據的準確性和可靠性(TGA,Code of GMP,2013)。
典型的PLC/HMI/SCADA – 數據管控措施
如下圖2所示,為確保數據完整性,在整個數據流過程:
1. 首先,需要受管控(如前文提到的帶時間戳的審計追蹤)的CGMP 電子數據是指該數據最終保存時間必需是執行CGMP操作同一時間(Data Integrity – ALCOA中 Contemporaneous同時性要求);所以PLC Transient 短暫Data不是,而SCADA中Saved Data 在是CGMP電子數據(21 CFR 211.100(b))。
2. SCADA上存儲的CGMP電子數據完整性需要帶時間戳的審計追蹤,數據管理,報警管理,記錄歸檔與恢復等數據管控措施( EU Annex 11 )。
3. PLC和HMI上的臨時短暫數據完整性則基于IT基礎設施確認(GAMP5:IT Infrastructure qualification),設備校驗,I/O準確性測試(EU Annex 15).
建議的措施
純設備or外加自控PLC
1.啟用前設備確認,生產中參數有記錄,任何修改有流程控制
2.周期性校驗傳感器和參數設置
3.Time Stamp - 生產區設置時鐘,定期校驗,操作員寫批次記錄時實時記錄
設備+PLC+HMI(最終數據存儲)
1.HMI 數據為CGMP E-data;需計算機化系統驗證 功能包括如用戶管理,權限隔離,帶時間戳的審計追蹤,數據管理,產生報告,報警管理,記錄歸檔與恢復等
2.如果受限于性能,上述審計追蹤,數據備份,權限功能實現不了,臨時措施可以以流程控制-操作日志本+紙質報告+簽字,長期來看,對重要設備需要做CSV技術升級改造(MES or SCADA)。
設備+PLC+HMI(單機)+SCADA(集成)
SCADA數據為CGMP E-data;需計算機化系統驗證 功能包括如用戶管理,權限隔離,帶時間戳的審計追蹤,數據管理,產生報告,報警管理,記錄歸檔與恢復等
免責聲明:上述內容僅供交流學習使用,對文中陳述、觀點判斷保持中立,不對所包含內容的準確性、可靠性或完整性提供任何明示或暗示的保證。僅作參考,并請各位自行承擔全部責任。版權歸原作者所有,如遇版權問題請聯系小編刪除。